Premise
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted the global business landscape, causing widespread disruptions and challenging organizations to adapt to unprecedented circumstances. The COVID-19 pandemic, which emerged in late 2019, rapidly spread across the globe, resulting in a severe health crisis. However, the pandemic’s effects extended beyond public health, significantly impacting the global economy and business environment. Specifically understanding the repercussions of this crisis on businesses through Porter’s Five Forces Framework is crucial for formulating effective strategies and ensuring long-term survival.
Definition of the Business Environment
The business environment refers to the external factors, such as economic, social, political, technological, and legal aspects, that influence a company’s operations and decision-making processes.
Importance of Analyzing the Business Environment
Analyzing the business environment enables organizations to identify potential risks, anticipate market trends, and leverage opportunities. This assessment forms the foundation for strategic planning and informed decision-making.
Factors Influencing the Business Environment
Factors that shape the business environment, include economic conditions, sociocultural trends, political and legal aspects, technological advancements, and ecological considerations.
Porter’s Five Forces Framework
Explanation of the Framework
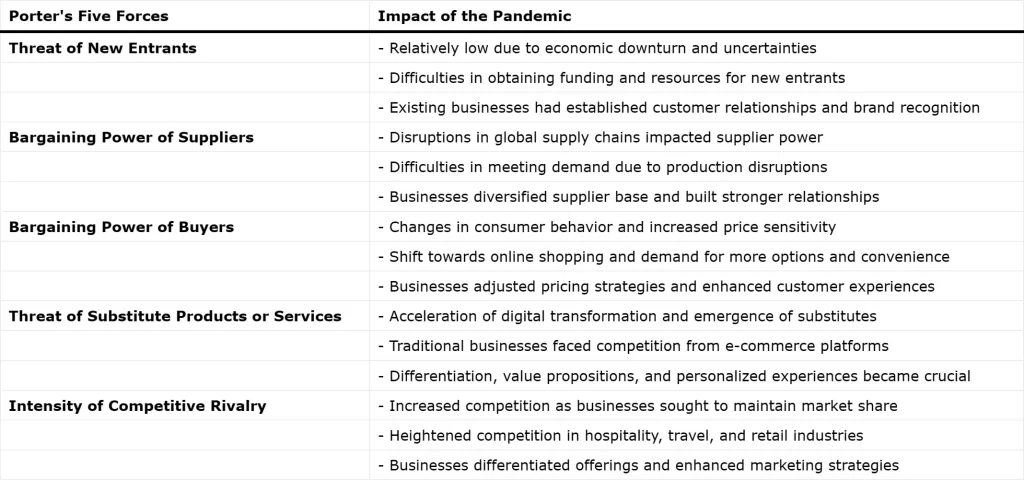
Threat of New Entrants:
During the pandemic, the threat of new entrants was relatively low in many industries due to the economic downturn and uncertainties. Start-ups and new businesses faced challenges in obtaining funding and resources, which acted as barriers to entry. Existing businesses also had the advantage of established customer relationships and brand recognition, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
The pandemic disrupted global supply chains, leading to fluctuations in the bargaining power of suppliers. In some cases, suppliers faced difficulties in meeting demand due to production disruptions or logistic constraints. But this shift in supplier power affected industries that heavily relied on international suppliers or those facing shortages of critical resources. Therefore, businesses had to diversify their supplier base and build stronger relationships to ensure a resilient supply chain.
Bargaining Power of Buyers:
Consumer behaviour underwent significant changes during the pandemic, affecting the bargaining power of buyers. Conversely, with increased uncertainty and financial constraints, consumers became more price-sensitive and demanding. Also, online shopping surged, giving consumers more options and convenience. Unquestionably then businesses had to adapt their pricing strategies, enhance customer experiences, and offer flexible payment options to retain customers and remain competitive.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
The pandemic accelerated digital transformation and innovation, leading to the emergence of substitute products and services. For instance, traditional brick-and-mortar retailers faced competition from e-commerce platforms. At this point, businesses had to embrace technology and develop online channels to reach customers and mitigate the threat of substitutes. Eventually, differentiation, unique value propositions, and personalized experiences became essential in retaining customers amidst a rapidly evolving landscape.
Intensity of Competitive Rivalry:
The pandemic intensified competitive rivalry as businesses sought to maintain their market share and survive in a challenging environment. Moreover, industries such as hospitality, travel, and retail experienced heightened competition due to reduced demand and changing consumer preferences. Chiefly Businesses had to differentiate their offerings, implement cost-cutting measures, and enhance marketing and customer engagement strategies to stand out and maintain profitability.
Conclusion
Indeed by applying Porter’s Five Forces Framework, businesses could assess the specific challenges and opportunities brought about by the pandemic, enabling them to develop effective strategies to navigate the changing business landscape and stay competitive.
If you liked this article, consider reading Business Management articles.